Types and Applications of Different Leadership Styles3/27/2020
In order to stay relevant in a competitive marketplace, companies must rely on strong leaders to motivate their employees.
Leaders may primarily engage their workforce with autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire and transformational leadership strategies. Alternatively, they may adopt transactional, task-oriented, situational, servant and charismatic leadership strategies to optimise their organisation’s productivity.
Instead of viewing each leadership style in isolation, leaders should combine or alter various leadership styles according to their organisation’s requirements.
Primary Leadership Styles
According to Researcher Kurt Lewin, managers may use the following leadership styles in different situations (MBA Caribbean Organisation, n.d.):
Autocratic Leadership Style
Autocratic Leaders are the only decision makers in their team. They establish a set of instructions that their teammates must follow, and their relationships with their teammates are strictly professional (Dyczkowska & Dyczkowski, 2018).
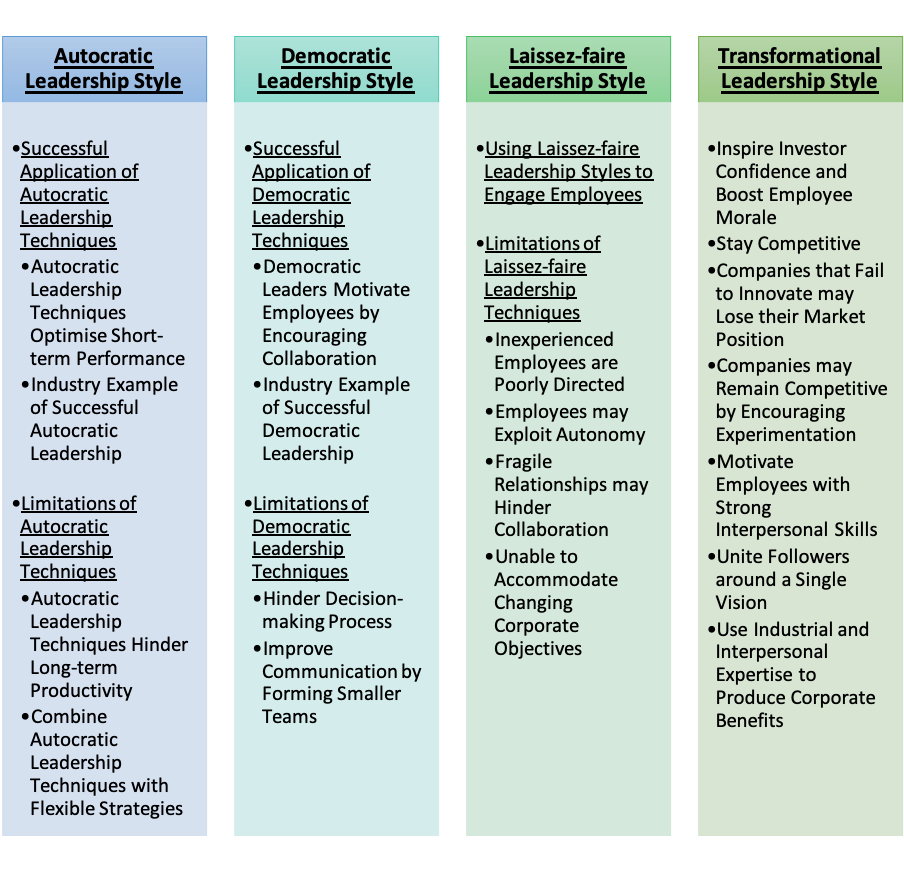
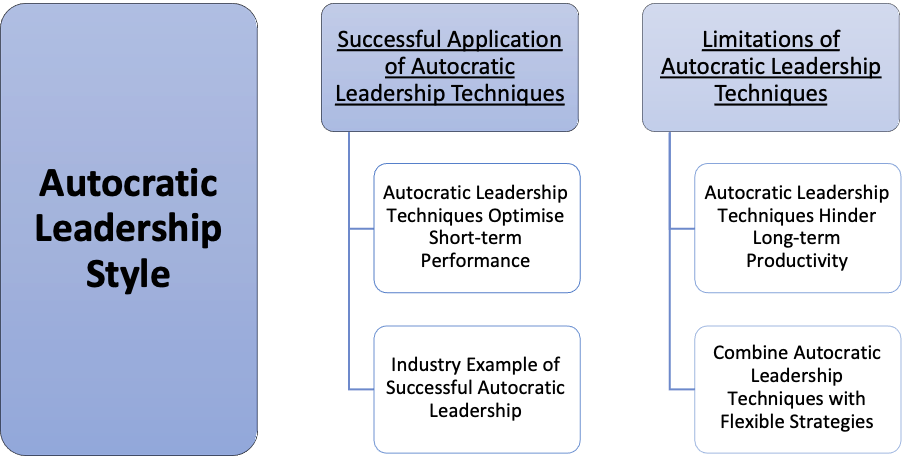
Successful Application of Autocratic Leadership Techniques Autocratic Leadership Techniques Optimise Short-term Performance Autocratic Leadership techniques may be used to deliver specified, summarised instructions on how employees should complete their tasks. These techniques ensure that employees can:
Industry Example of Successful Autocratic Leadership Martha Stewart is regarded as a successful Autocratic Leader. She assumed control of multiple facets of her programmes, and she required little input from her subordinates. Although her authoritative leadership style has been criticised, it has allowed her to succeed in a competitive entertainment industry (Chris, 2015). Limitations of Autocratic Leadership Techniques Autocratic Leadership Techniques Hinder Long-term Productivity Autocratic Leadership techniques may increase short-term productivity, but its formalised rules and procedures do not encourage creative thinking within organisations (Sauer, 2011). This may severely affect the long-term growth of Small-and-Medium-Sized Enterprises (SMEs), which rely on an innovative workforce and a flexible work environment in order to compete in their dynamic industries. Combine Autocratic Leadership Techniques with Flexible Strategies In order to address this issue, managers should adopt Autocratic Leadership techniques during the early stages of their company’s growth, in which employees require instruction and direction to complete their tasks. Once their employees are familiar with their corporate procedures, managers should adopt alternative leadership styles that would give their staff more freedom to act. Democratic Leadership Style
Democratic Leaders make critical decisions on behalf of a team. However, they would also involve their employees in their decision-making process. They adopt a collaborative approach that guides their team towards its objectives.
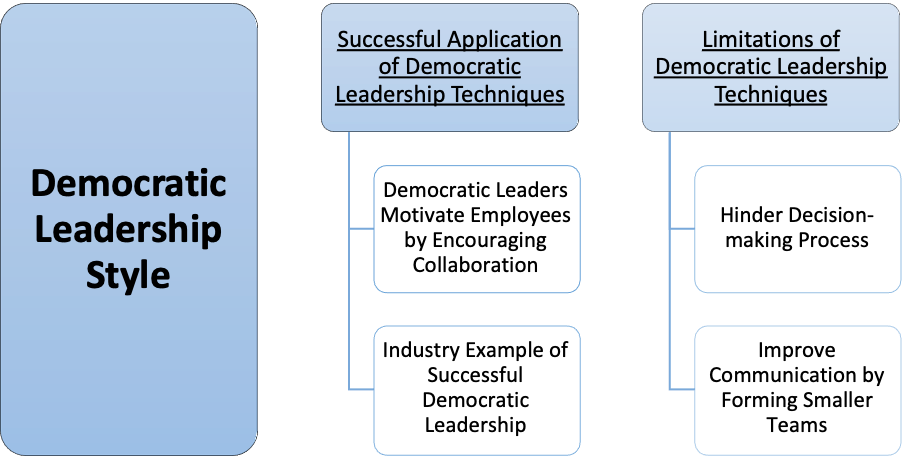
Successful Application of Democratic Leadership Techniques Democratic Leaders Motivate Employees by Encouraging Collaboration Democratic Leaders encourage collaboration within their teams, and they tend to consult their subordinates before making critical decisions (Cellar et al., 2001; Maloş, 2012). Instead of penalising mistakes, they reward employees according to their commitment to the firm, and their ability to devise solutions to their problems. These strategies motivate their staff to meet their performance objectives (İnandi et al., 2016). Industry Example of Successful Democratic Leadership Sergey Brin and Larry Page, founders of Google, hired experienced professionals that could allow their company to grow. Although they were Google’s primary decision makers, they considered the advice of their seasoned teammates, and developed a collaborative culture that fostered innovation within their organisation (St. Thomas University, 2014a). Limitations of Democratic Leadership Techniques Hinder Decision-making Process Democratic Leadership techniques may give employees a sense of ownership, but they may also slow down the decision-making process. Managers may face difficulty with integrating multiple opinions into their final verdict. Furthermore, multiple stakeholders may have conflicting perspectives, which may create tension during brainstorming sessions or team-building initiatives. Improve Communication by Forming Smaller Teams In order to address these issues, Democratic Leaders should consider forming smaller teams, which would allow better communication between their employees (Fiaz et al., 2017). This would allow leaders to promote mutual understanding between their subordinates and inform their employees about key performance objectives. Laissez-faire Leadership Style
Using Laissez-faire Leadership Styles to Engage Employees
Once an organisation’s employees are properly informed and trained, leaders may allocate more control to their subordinates. This may be achieved with Laissez-faire Leadership strategies, which allow team members to make decisions and implement solutions on their leader’s behalf. By providing employees with autonomy during the decision-making process, Laissez-faire leaders are able to promote a sense of ownership amongst their workforce. This would allow their organisations to retain competent staff members, and boost employee morale (Kowalski & Cangemi, 1993; cited in Hollander Vineburgh, 2010). Limitations of Laissez-faire Leadership Techniques Although Laissez-faire Leadership techniques can promote autonomy and innovation, they may be hindered by the following factors: Inexperienced Employees are Poorly Directed: Laissez-faire leaders may not be able to lead inexperienced staff members. Inexperienced employees who do not receive sufficient instructions may make poor decisions, which may affect the reputation of their leader or company. Employees may Exploit Autonomy: Employees may be tempted to exploit the freedom that they are provided. Due to the absence of formal rules or penalties, they may not be motivated to optimise their performance (Schyns & Schilling, 2013). Fragile Relationships may Hinder Collaboration: Leaders who do not actively build relationships with their employees may fail to foster trust within their team. This fragile camaraderie may discourage their teams from collaborating with each other during difficult situations (Gillespie and Mann, 2004). Unable to Accommodate Changing Corporate Objectives: Robert Noyce, co-founder of Intel, possessed a Laissez-faire management style that inspired employees from his previous company to join him. Unfortunately, Noyce’s Laissez-faire management style was not suitable as Intel began to grow. The company’s objectives shifted towards producing quality products and achieving of economies of scale, which may be obtained with a democratic leadership style (St. Thomas University, 2014b). Transformational Leadership
Transformational Leaders are highly inspirational, and they can motivate their followers to achieve ambitious goals and positive results (Robbins et. al, 2016).
According to Odumeru & Ifeanyi (2013), Transformational Leaders:
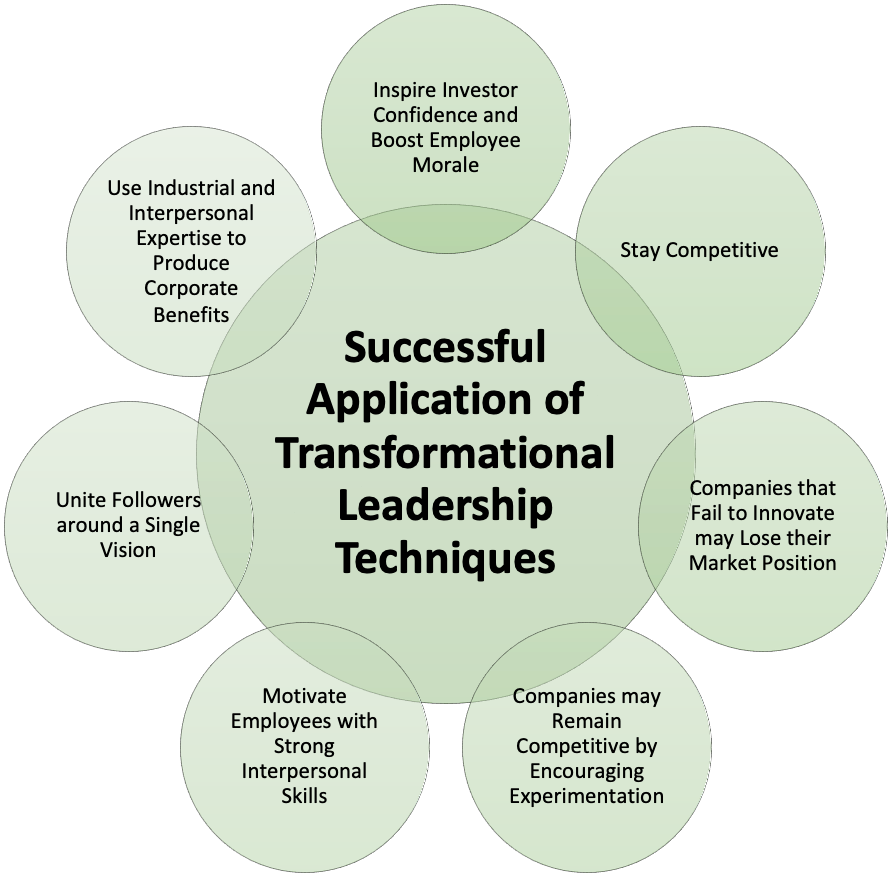
Successful Application of Transformational Leadership Techniques Transformational Leaders may produce the following benefits for their organisations: Inspire Investor Confidence and Boost Employee Morale Mark Bertolini, CEO of Aetna, uses his storytelling skills to communicate his organisation’s vision to its key stakeholders. He uses persuasive techniques to explain how Aetna’s customers would be able to make better health choices, and how its new business model of value-based care can change the nature of health insurance (Anthony & Schwartz, 2017). By promoting the societal importance of his company’s operations, Bertolini boosts investor confidence, and motivates his employees to maximise their performance. Stay Competitive Companies that Fail to Innovate may Lose their Market Position Leaders may use Transformational strategies to spark innovation within their organisations. According to Anthony and Schwartz (2017), companies that fail to implement Transformational Strategies may falter against innovative competitors. For instance, Blockbuster’s inability to combat the emergence of Over-the-top (OTT) media services caused it to lose its market share to Netflix. Companies may Remain Competitive by Encouraging Experimentation Alternatively, companies that embrace Transformational risk-taking and exploration may sustain their competitive positions. For example, Satya Nadella, CEO of Microsoft, encourages continuous experimentation within his organisation. As a result, Microsoft’s products possess multiple features and improvements, which gives them a competitive edge in their expanding industry (Anthony & Schwartz, 2017). Motivate Employees with Strong Interpersonal Skills Transformational Leaders have strong interpersonal skills, which allows them to attend to their employees’ needs. Furthermore, Transformational Leaders may motivate their workforce by acknowledging their employees’ individual contributions. For instance, Microsoft’s Nadella is an effective listener who inspires his subordinates through experimental projects, such as company-wide hackathons, and empowers them to develop projects that they are passionate about (Anthony & Schwartz, 2017). Leaders with strong interpersonal skills ensure that employees gain a sense of purpose, which may allow teams to optimise their productivity and growth. Unite Followers around a Single Vision Transformational leaders are respected by their subordinates, and they can boost their followers’ morale by uniting their staff around their vision. John D. Rockefeller, the founder of Standard Oil, united his workforce with a single corporate vision. He drove his workforce towards his corporate vision by fostering a sense of ownership amongst his employees, and by implementing strong corporate strategies (St. Thomas University, 2014c). Use Industrial and Interpersonal Expertise to Produce Corporate Benefits Transformational Leaders possess industrial and interpersonal expertise, and may use their expertise to:
Additional Leadership Styles
Table View of Additional Leadership Styles
Transactional Leadership
Task-oriented Leadership
Situational Leadership
Servant Leadership
Charismatic Leadership
Combining Different Leadership Strategies
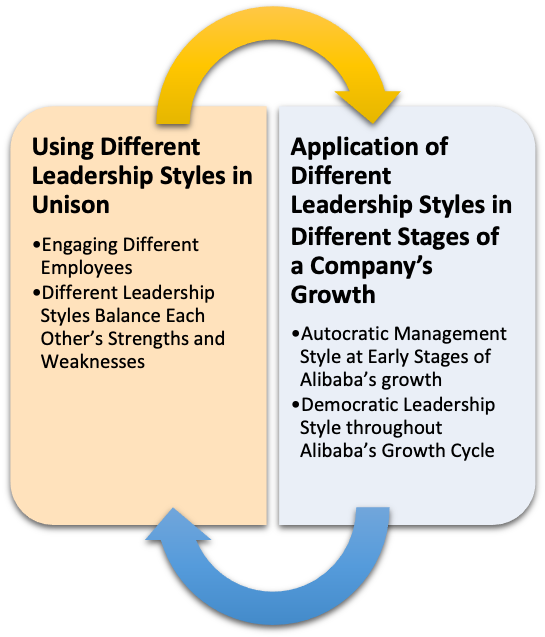
Different leadership frameworks must not be used in isolation. Instead, various leadership frameworks may be used in unison, or they may be adjusted according to the stages of their company’s growth.
Using Different Leadership Styles in Unison
Engaging Different Employees
According to researcher Van Dierendonck et al. (2014), leaders may engage their employees by combining multiple leadership styles. Employees may have different reactions to specific leadership styles, and supervisors may engage their entire workforce by adopting a multifaceted leadership approach. This ensures that employees are more committed and enthusiastic about an organisation’s activities. Different Leadership Styles Balance Each Other’s Strengths and Weaknesses Furthermore, each leadership technique has certain strengths that may offset the limitations of other management styles. For example, organisations may overcome crises by using a transformational leader’s insight to devise innovative strategies. At the same time, they may use a servant leader’s benevolence to boost employee morale (Van Dierendonck et al., 2014). Application of Different Leadership Styles in Different Stages of a Company’s Growth Jack Ma, founder and CEO of Alibaba, used the following management styles during different stages of his company’s development: Autocratic Management Style at Early Stages of Alibaba’s growth During the early stages of a company’s growth, Ma’s employees required instruction and direction. As such, he chose to adopt an autocratic management style. This ensured that he was his team’s primary decision maker, and he required little input from his subordinates. Democratic Leadership Style throughout Alibaba’s Growth Cycle As Alibaba began to grow, Ma adopted a democratic leadership style, which allowed his co-directors and managers to control different aspects of Alibaba’s operations. This allowed his team to experiment with different strategies and solutions that improved Alibaba’s productivity (Tham & Yazdanifard, 2015). Conclusion
Leaders motivate their employees with autocratic, democratic, laissez-faire and transformational leadership strategies. They may also consider using transactional, task-oriented, situational, servant and charismatic leadership strategies to improve their workforce’s productivity.
In order to optimise the strengths and address the weaknesses of each leadership style, supervisors may choose to combine multiple techniques, or they may alter their strategy according to the stage of their company’s growth. This would enable them to develop a holistic leadership strategy, which would drive their teams towards their corporate goals.
references
0 Comments
Leave a Reply. |
Join Our Mailing List
Receive fresh insights about finance, HR and strategic planning.
Contact UsBusiness Intelligence and 8nalytics Pte Ltd © 2021
Email
admin@8nalytics.com Location 190 Middle Road #16-08 Fortune Centre Singapore 188979 Phone +65 6255 5101 +65 9655 8948 |
Sitemap |